NASAL BONES
Lateral Projection • Nasal trauma evaluation • Nasal bone fractures
Exposure Factors
Note: Low exposure parameters for maximum bone detail
Plate Size
Small plate for tight collimation and dose reduction
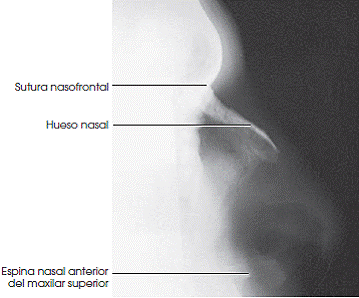
Visible Anatomical Structures
Nasal Bones
Proper nasal bones
Soft Tissues
Nasal soft structures
Nasal Spine
Anterior nasal spine
Suture
Nasofrontal suture
Quality evaluation:
- Bones and soft parts of the nose without rotation
- Anterior nasal spine clearly visible
- Identifiable nasofrontal suture
- Symmetric structures when comparing both sides
MANDATORY BILATERAL COMPARISON
Both sides (right and left) must be examined and compared to:
- Detect subtle asymmetries
- Compare bone density
- Evaluate alignment
- Identify minimal displacements
Important: Always perform projections of both sides in nasal trauma
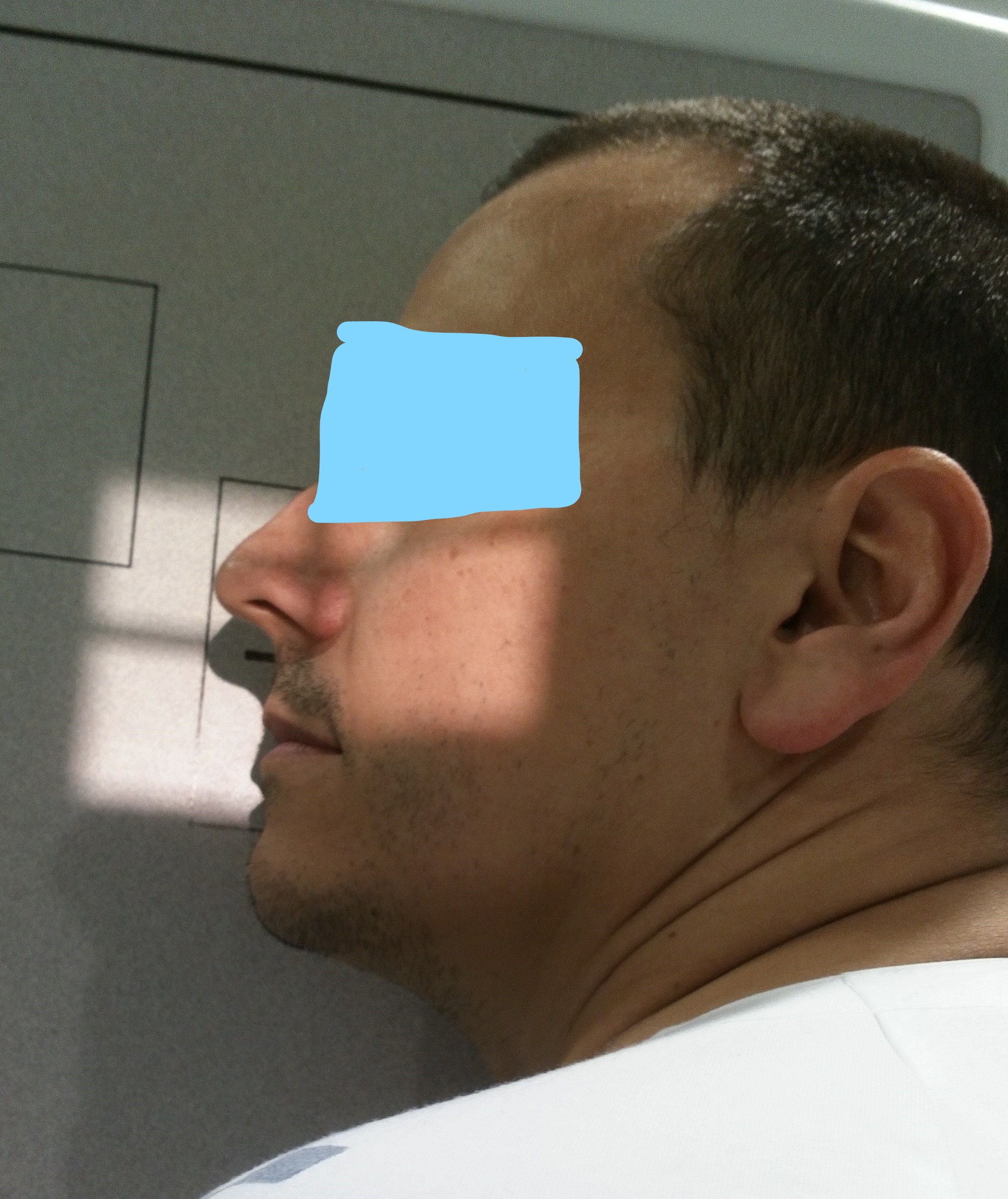
Patient Positioning
Exact Central Ray Point
Nasion: Junction point between nasal bones and frontal
Distal: Toward tip of nose from nasion
Location: Approximately at mid-nasal bridge
Measurement: 1.3 cm from frontonasal junction downward
TIGHT COLLIMATION
Tight collimation is used
Limited to the nasal bone area for:
- Significant patient dose reduction
- Better contrast and bone detail
- Less radiation scatter
- Sharper image of small structures
Protection: Collimate only to nasal area - protect eyes and teeth
Central Ray Direction
PERPENDICULAR to the nasal bridge
Angle: 90° to nasal bridge plane
No angulation - Direct to specified point
Patient Instructions
"Hold your breath during exposure"
Maintain complete immobility - Do not move head or nose during exposure
Nasal Trauma Considerations
Active Bleeding
If active nasal bleeding, postpone study or use additional protection.
Pain
Position carefully, avoid excessive pressure on traumatized nose.
Minimal Fractures
Careful search for non-displaced fractures or soft tissue infiltration.